Multi-Factor Authentication
Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication provides a means to verify who you are using more than just a username and password. It provides a second layer of security to user sign-ins. In order for users to be able to respond to MFA prompts, they must first register for Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication.
The MFA becomes inevitable in present situation, as the chance of compromise is likely less than 99.99%.
How to enable the AAD MFA:
We can enable the MFA in Azure AD portal or Office 365 portal through multiple ways. For that, we need to fulfil the below prerequisites.
Prerequisites to enable the AAD MFA:
1.To manage MFA fully, one should be global administrator. But some of the MFA settings can be managed by Authentication policy administrator and Per user MFA can be managed by the Authentication administrator and privileged authentication administrator.
- License:
| Method to Enable MFA | License Required |
| Security Defaults | Free tier of AAD |
| Per user MFA | Azure AD Premium P1 or similar licenses that include this functionality such as Enterprise Mobility + Security E3, Microsoft 365 F1, or Microsoft 365 E3 |
| Conditional Access policy | Azure AD Premium P1 or similar licenses that include this functionality such as Enterprise Mobility + Security E3, Microsoft 365 F1, or Microsoft 365 E3 |
| Risk based conditional Access policy | Azure AD Premium P2 |
| Device Settings | Azure AD Premium P1 |
| AAD Identity Protection MFA registration Policy | Azure AD Premium P2 |
Ways to enable AAD MFA:
The following ways are used to enable Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication for your Azure Active Directory (AD) users based on the licenses that your organization owns.
1.Per user MFA
We can do this in AAD or Office 365 portal. Here, we can change and review the state of a user by enabling and disabling the per user MFA.
First of all, we should know about enable, disable and enforce of MFA.
2.Conditional access policy
Comes with Azure AD Premium P1 or similar licenses that include this functionality such as Enterprise Mobility + Security E3, Microsoft 365 F1, or Microsoft 365 E3
*For customers with AZURE AD Premium P2 – can use Risk based conditional access policy for enabling the MFA.
Through Conditional access policy, we can enable to MFA for users that means we can give granular control of access to the users. That is, we can put rules to control the users.
In rules, we can include and exclude the user and groups to enable MFA.
We can apply conditional access policy: Azure Active Directoryà Security à Conditional Access.
Here is the real time scenario: Some users in the organization needs to access the outlook only by desktop app (not OWA).
In assignments:
User & groups: we can select (include) those users and exclude others
Cloud apps or actions: we can select the Outlook desktop app
In Controls:Grant: we can grant the access and check the box REQUIRE MFA.
That means, users can access the outlook in desktop app only when the MFA enforced.
3.Security defaults:
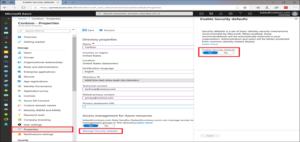
Security default is an option in Azure AD which is to enable the MFA for all users in Azure AD. Microsoft is making security defaults available to everyone. The goal is to ensure that all organizations have a basic level of security enabled at no extra cost. That means, to enable the MFA with security defaults, we just need AAD free trail.
To turn on Security defaults – go to Azure AD admin centreàpropertiesàManage security defaults and turn on.
Azure AD MFA registration policy
Identity Protection can help organizations roll out Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) using a Conditional Access policy requiring registration at sign-in. Enabling this policy is a great way to ensure new users in your organization have registered for MFA on their first day. Multi-factor authentication is one of the self-remediation methods for risk events within Identity Protection. Self-remediation allows your users to take action on their own to reduce helpdesk call volume.
Azure Active Directory Identity Protection includes three default policies that administrators can choose to enable.
We can enforce this by following this path in Azure AD:
Azure Active DirectoryàSecurityàIdentity ProtectionàMFA registration policy.
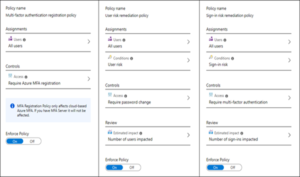
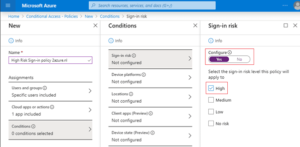
Risk Based conditional access:
Risk based Conditional Access to assign risk levelbased options to your policies. Azure AD Identity Protection can detect six different types of suspicious sign-in activities with 3 different levels of risks. These conditions will be available only if we have Azure AD premium P2 license.
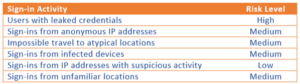
With the risk levels combined with conditional access policies we can protect sensitive application and data access.

Note: To enforce the sign in remediation policy
Ways of authentication Methods:
The following are the ways of various authentication methods for additional verification of user during the sign in process. Depending on the way of enabling the MFA, the authentication method available. The below table, clearly give the picture of this.
Note: we can’t use security questions as the way of authentication method for AAD MFA. It can be used only for SSPR.
| Method | Security defaults | All other methods |
| Notification through mobile app | X | X |
| Verification code from mobile app or hardware token | X | |
| Text message to phone | X | |
| Call to phone | X |
The registration for MFA:
User needs to register the next time they sign in interactively and they will have 14 days to complete registration. During this 14-day period, they can bypass registration if MFA is not required as a condition, but at the end of the period they will be required to register before they can complete the sign-in process.
MFA settings:
We can customize the end user experience through AAD MFA. Some settings are available directly in the Azure portal for Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), and some are in a separate Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication portal. The following are various features provided by Azure AD MFA.
| Feature | Description |
| Account lockout | Temporarily account will be locked if there are too many denied authentication attempts in a row. |
| Block/unblock users | Block specific users from being able to receive Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication requests. Any authentication attempts for blocked users are automatically denied. Users remain blocked for 90 days from the time that they’re blocked or until they’re manually unblocked. |
| Fraud alert | Configure settings that allow users to report fraudulent verification requests. |
| Notifications | Enable notifications of events from MFA Server. |
| OATH tokens | Used in cloud-based Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication environments to manage OATH tokens for users. |
| Phone call settings | Configure settings related to phone calls and greetings for cloud and on-premises environments. We can customize the end user experience. |













